CLIP-170S is a microtubule +TIP variant that confers resistance to taxanes by impairing drug-target engageme

CLIP-170 tracks growing microtubule ends by dynamically recognizing composite EB1/tubulin-binding sites | Journal of Cell Biology | Rockefeller University Press
Overexpression of the microtubule-binding protein CLIP-170 induces a +TIP network superstructure consistent with a biomolecular condensate | PLOS ONE
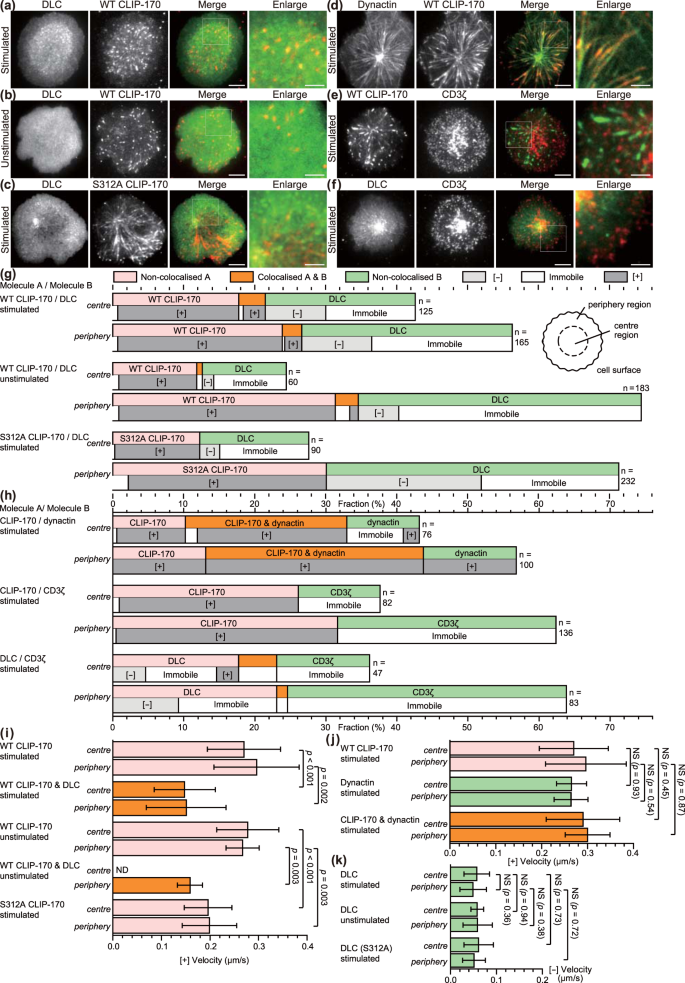
CLIP-170 is essential for MTOC repositioning during T cell activation by regulating dynein localisation on the cell surface | Scientific Reports
Domain architecture of CLIP-170 and EB1. A, domain architecture of EB1... | Download Scientific Diagram

CLIP-170S is a microtubule +TIP variant that confers resistance to taxanes by impairing drug-target engagement - ScienceDirect
Overexpression of the microtubule-binding protein CLIP-170 induces a +TIP network superstructure consistent with a biomolecular condensate | PLOS ONE

Model of phosphorylation-mediated autoinhibition of CLIP-170. CLIP-170... | Download Scientific Diagram

Arsenic trioxide disturbs the LIS1/NDEL1/dynein microtubule dynamic complex by disrupting the CLIP170 zinc finger in head and neck cancer - ScienceDirect

Microtubule binding proteins CLIP-170, EB1, and p150Glued form distinct plus-end complexes - ScienceDirect

α-Tubulin Tyrosination and CLIP-170 Phosphorylation Regulate the Initiation of Dynein-Driven Transport in Neurons - ScienceDirect

CLIP‐170 spatially modulates receptor tyrosine kinase recycling to coordinate cell migration - Zaoui - 2019 - Traffic - Wiley Online Library












